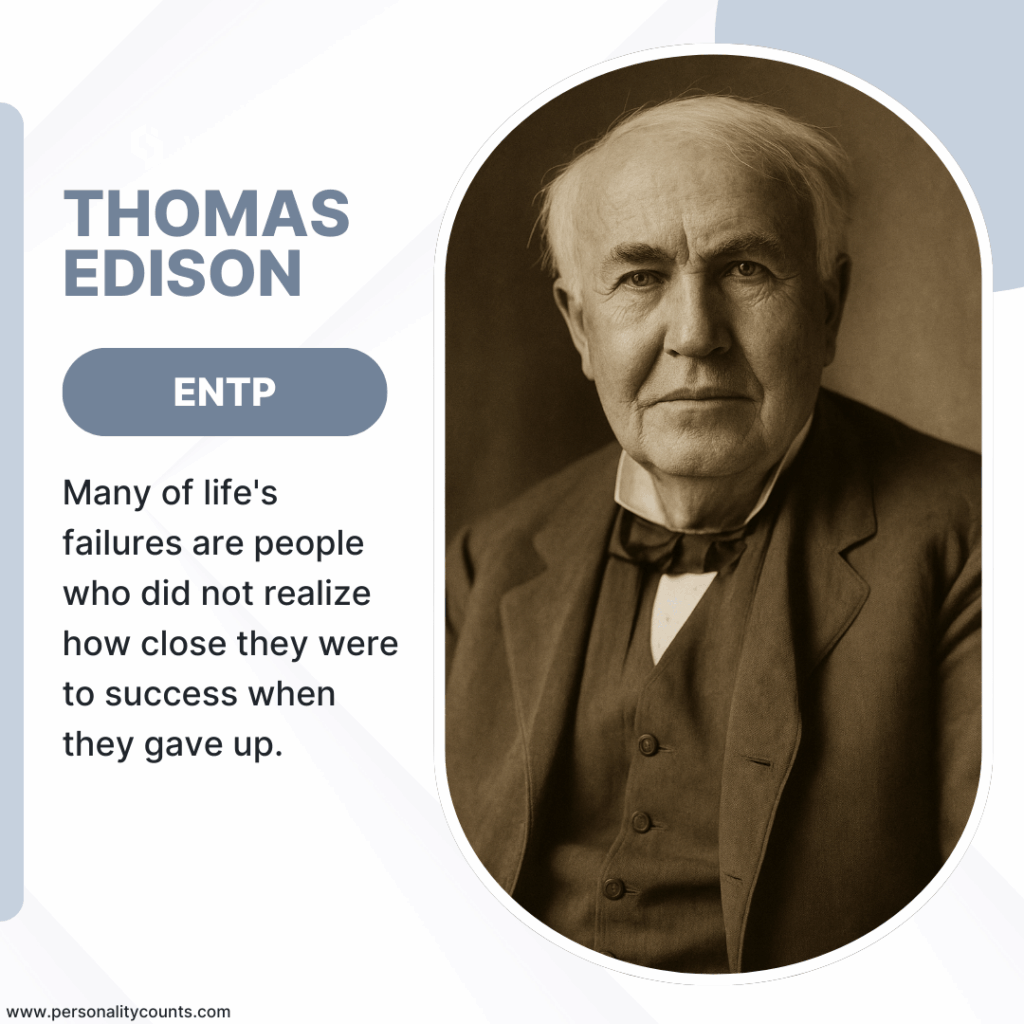
ENTP
ENTPs are innovators, idea-generators, and problem-solvers. They thrive on experimentation, debate, and breaking old systems to create new ones. Thomas Edison, one of history’s most prolific inventors, embodies the ENTP personality type. Known for his curiosity, resilience, and relentless drive, Edison’s mind never stopped generating possibilities. His contributions to electricity, sound recording, and motion pictures reshaped modern life and illustrate the adventurous and visionary traits of the ENTP personality.
Origins and Early Life
Thomas Alva Edison was born in 1847 in Milan, Ohio, and raised in Port Huron, Michigan. He was the youngest of seven children and showed curiosity early on. Though considered a poor student, Edison had a restless imagination and preferred hands-on experimentation over traditional schooling. His mother encouraged self-education, which fit his ENTP need for exploration outside rigid systems.
By his teens, Edison was already tinkering with chemistry sets and mechanical devices, selling newspapers and candy on trains to fund his experiments. This entrepreneurial streak—hallmark ENTP resourcefulness—would define his career.
Thomas Edison with the Light Bulb – Oil Painting Artwork

This oil painting artwork captures Thomas Edison in his laboratory, holding the glowing light bulb that changed the world. The warm tones and realistic brushstrokes highlight his determination and inventive genius, while the shelves of early electrical equipment symbolize the relentless experimentation behind his breakthroughs. Edison’s ENTP personality is reflected in the creativity, energy, and boldness conveyed by the painting—reminding us how vision and persistence can shape history.
Inventions and Achievements
Edison held over 1,000 patents, making him one of the most prolific inventors in history. His ability to brainstorm, experiment, and adapt aligns with ENTP traits of curiosity, resilience, and fearlessness in trial and error.
Some of his most famous contributions include:
- The Phonograph (1877) – Revolutionized sound recording and playback. Edison called it his favorite invention.
- The Incandescent Light Bulb (1879) – While not the first to attempt it, Edison perfected and commercialized the light bulb, making electric lighting practical.
- The Motion Picture Camera (Kinetoscope) – Helped launch the film industry by making moving images possible.
- Electric Power Systems – His work on direct current (DC) distribution systems changed cities, bringing light and power into everyday life.
These achievements reveal the ENTP ability to connect ideas, challenge existing systems, and keep iterating until something works.
Entrepreneurial Spirit
Edison wasn’t just an inventor—he was also a shrewd businessman. He founded General Electric, one of the most influential corporations in history. Unlike some inventors who focus only on ideas, Edison combined creativity with practical strategy, ensuring his inventions reached the masses.
This reflects the ENTP blend of vision (Ne) and logic (Ti). Edison not only created new technologies but also found ways to commercialize them, shaping industries that continue today.
Thomas Edison’s ENTP Cognitive Functions
- Ne (Extraverted Intuition) – Lead Function
Edison constantly generated new possibilities. His mind leapt from one idea to another, seeing connections others missed. His thousands of patents show Ne in action. - Ti (Introverted Thinking) – Secondary Function
He analyzed problems systematically, refining his ideas through structured experiments. Ti gave his creativity precision. - Fe (Extraverted Feeling) – Tertiary Function
Though not always warm in personal relationships, Edison inspired and led large teams of workers and collaborators. Fe allowed him to rally people around his vision. - Si (Introverted Sensing) – Inferior Function
Edison was less interested in tradition or consistency. He preferred innovation over stability, though he relied on past data during long experimentation processes.
Controversies and Rivalries
Like many ENTPs, Edison was not without controversy. He clashed with Nikola Tesla over direct current (DC) versus alternating current (AC), a rivalry remembered as the “War of Currents.” Edison fiercely defended his vision, sometimes using questionable tactics.
Critics argue Edison received more credit than he deserved, often building on the work of others. Still, his persistence, entrepreneurship, and ability to scale ideas were uniquely his. The controversies reflect both the brilliance and flaws of ENTPs—driven, competitive, and sometimes too focused on winning.
Interesting Facts About Thomas Edison
- He considered sleep a waste of time, often working through the night.
- Was mostly deaf, but he claimed this helped him concentrate better.
- Created the first industrial research lab in Menlo Park, pioneering team-based innovation.
- Coined the phrase: “Genius is one percent inspiration and ninety-nine percent perspiration.”
- Had limited formal schooling, yet became one of history’s most celebrated minds.
Lessons Fans Can Learn from Thomas Edison
- Experiment constantly – don’t fear failure; each attempt teaches something.
- Think big, then refine – vision plus persistence leads to breakthroughs.
- Combine creativity with practicality – innovation matters most when it improves lives.
- Resilience is key – Edison’s thousands of failed attempts remind us persistence often precedes success.
Famous Quotes
“I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work.”
An ENTP reminder that failure is simply data in disguise.
“Genius is one percent inspiration and ninety-nine percent perspiration.”
Captures the ENTP balance of bold vision and relentless effort.
